Experiencing double vision can be worrying, especially if it begins to affect daily activities like reading, driving, or even walking. While it may seem minor initially, it can sometimes indicate underlying health conditions that need attention. With specialized eye care easily accessible, early diagnosis and double vision treatment can help manage the condition effectively.
Here, we’ll cover the types of double vision, what neurological conditions cause double vision, available treatment options, and more.
Need Professional Help for Double Vision?
Book your appointment at Planet Lasik today!
What is Double Vision or Diplopia?
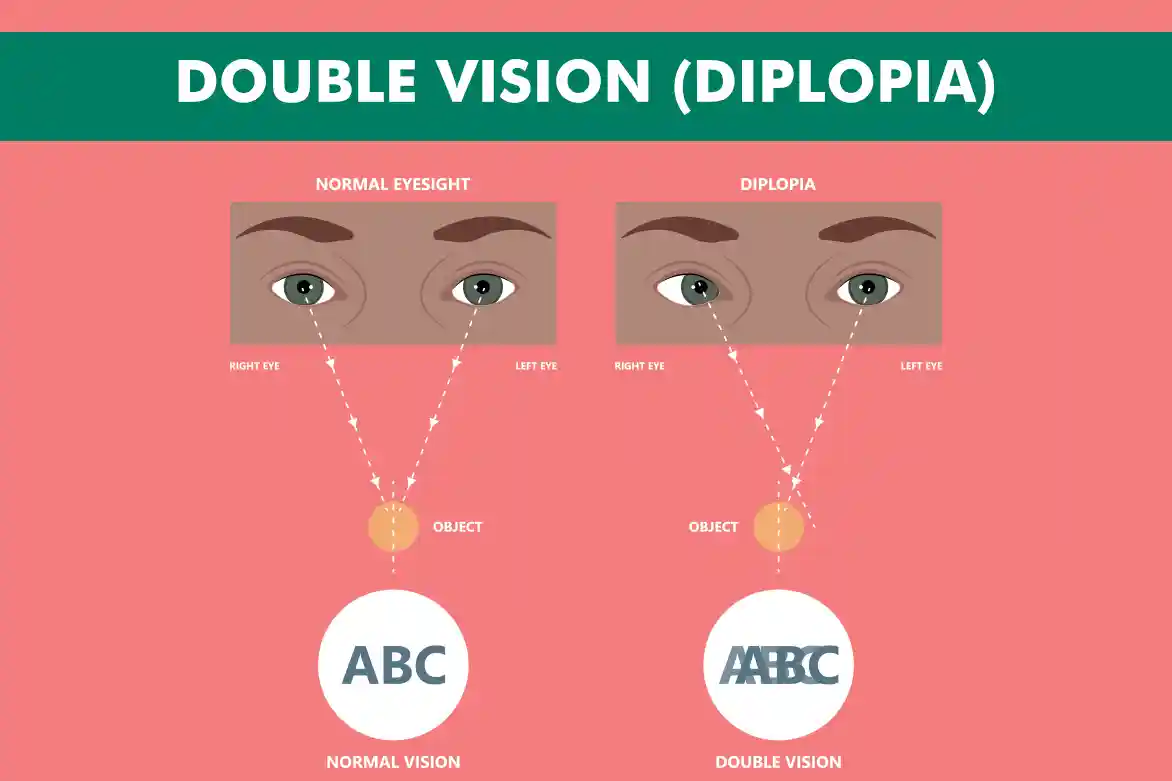
Double vision, also called diplopia, is a condition where your eyes see two images of a single object. These images can be side by side or overlap, which makes daily tasks like reading or driving difficult. Double vision can impact one eye or both, depending on the cause.
Types of Diplopia
Diplopia can be classified into two main types: monocular and binocular.
Monocular Diplopia
Monocular diplopia is a form of double vision that occurs when a person experiences double vision in one eye, even when the other eye is closed. This is the most common type of double vision and is generally less concerning than binocular diplopia, which happens with both eyes open.
Typical causes of monocular diplopia include:
- Refractive errors like astigmatism
- Changes in the shape of the eyeball
- Cataract-related changes in the eye’s natural lens
- Corneal surface irregularities, such as keratoconus or untreated astigmatism
Monocular diplopia can make daily activities, like driving or reading, more difficult and may increase the likelihood of falls. However, most people with this condition recover fully, often with minimal intervention.
Binocular Diplopia
Binocular diplopia, commonly called double vision, occurs when a person sees two images while both eyes are open, but the double vision disappears when one eye is closed.
The condition is typically caused by misalignment of the eyes, also known as strabismus or squint. The nature of the double vision varies depending on the direction of the misalignment:
- Horizontal Misalignment: The two images appear next to each other, side by side.
- Vertical Misalignment: One image is positioned above the other.
- Diagonal Misalignment: The images are displaced both horizontally and vertically, resulting in a diagonal separation.
What Causes Diplopia?
Diplopia can occur due to underlying conditions. These issues affect how the eyes work together, or how the brain processes visual information. Identifying the reasons for double vision is vital for determining the appropriate diplopia treatment.
Some of the common causes of diplopia include:
- Eye muscle problems: Weak or misaligned eye muscles can cause the eyes to focus incorrectly.
- Nerve damage: Nerve damage, especially the nerves that control eye movement, can lead to diplopia.
- Brain issues: Conditions like strokes, tumors, or multiple sclerosis can interfere with the brain’s ability to process vision.
- Refractive errors: Cataracts or astigmatism can cause double vision in one eye (monocular diplopia).
- Trauma or injury: Head or eye injuries can result in diplopia by damaging the muscles or nerves involved in eye movement.
What are the Symptoms of Diplopia?
You may notice some of these common double vision symptoms:
- Seeing double images (either side by side or one above the other)
- Blurred vision
- Headaches
- Eye strain or discomfort
- Difficulty focusing
- Sensitivity to light
- Dizziness or trouble with balance
These symptoms can vary based on what’s causing it.
How is Diplopia Diagnosed?
To diagnose diplopia, your doctor will ask about your double vision symptoms and medical history, followed by a detailed eye exam. They may need further tests to understand the causes and determine the best treatment.
Here are some tests commonly used:
- Eye examination: To check for problems with vision, eye movement, or alignment.
- Neurological evaluation: To rule out any brain or nervous system issues that could cause diplopia.
- Blood tests: To test for infections or other health conditions.
- Imaging scans (MRI, CT scan): To closely examine the brain and eye structures.
Visit the nearest branch to get help and maintain proper eye health.
How is Diplopia Treated?
The treatment for diplopia depends on what’s causing it. If the issue is related to the eyes, like misalignment or focusing problems, eyeglasses or prism lenses might help correct the problem. Surgery could be needed to improve eye movement and alignment in cases where muscle or nerve damage is involved. Sometimes, treating underlying health conditions like stroke or diabetes can help resolve double vision. For those wondering how to cure double vision naturally, some may benefit from eye exercises and therapies, which aim to strengthen the eye muscles and improve coordination, but this depends on the severity of the condition.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you suddenly experience double vision, seeking medical advice is important. This could signify a more serious issue that needs prompt attention. Don’t wait, especially if you notice:
- Sudden onset of double vision
- Severe headaches
- Difficulty moving your eyes
These symptoms should be addressed as soon as possible to avoid further complications.
Whether it’s due to an eye issue or another health condition, prompt treatment can have a significant impact. Planet Lasik offers expert care across India.
Find out the cost of treatments and surgeries available at Planet Lasik.
FAQs
1. How can I stop double vision?
Double vision treatment depends on the cause. Options include prism lenses, eye exercises, or surgery for muscle or nerve issues. In some cases, managing underlying conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure can resolve the problem.
2. What deficiency causes double vision?
Low vitamin B12 can sometimes impact the optic nerve and cause double vision. Vitamin deficiencies can lead to nerve damage, so proper nutrition is important for eye health.
3. Is double vision myopia?
No, it is not the same as myopia (nearsightedness). Myopia affects distance vision, while double vision involves seeing two images of the same object. Both conditions need different treatments.