Refractive surgery includes a range of procedures that can help fix common vision issues like nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. By reshaping the cornea or adding a lens, these surgeries can often reduce or even do away with the need for glasses or contact lenses.
Thanks to the latest advancements in medical technology, refractive surgery has become a popular option for those looking to get rid of their glasses, enhance their vision, and enjoy a better quality of life.
Understanding Refractive Errors
Refractive errors occur when the eye cannot properly focus light on the retina, leading to blurred vision. The primary types of refractive errors include myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism. Myopia results in difficulty seeing distant objects clearly, hyperopia affects the ability to see nearby objects, and astigmatism causes distorted or blurred vision at all distances.
These errors are often due to the shape of the cornea or the length of the eye and can be effectively addressed through various refractive surgery techniques.
Common Vision Problems Addressed by Refractive Surgery
Refractive surgery can address a variety of vision problems, each with its own characteristics and challenges. Let’s explore them one by one:
Myopia (Nearsightedness):
This condition makes it difficult to see distant objects clearly. It occurs when the eye is too long or the cornea is too curved, causing light to focus in front of the retina. Refractive surgery can correct this by reshaping the cornea, allowing light to focus directly on the retina, thus improving distance vision.
Hyperopia (Farsightedness):
Individuals with hyperopia struggle to focus on nearby objects. This happens when the eye is too short or the cornea is not curved enough, causing light to focus behind the retina. Surgical procedures can adjust the cornea’s shape to ensure light focuses correctly on the retina, enhancing near vision.
Astigmatism:
This condition results in distorted or blurred vision at all distances due to an irregularly shaped cornea or lens. Refractive surgery can smooth out these irregularities, allowing light to focus evenly on the retina, which sharpens vision.
Presbyopia (Age-related Farsightedness):
As people age, the eye’s lens becomes less flexible, making it harder to focus on close objects. While not a refractive error in the traditional sense, certain surgical techniques can help manage presbyopia by adjusting the eye’s focusing ability.
Each of these vision issues can be significantly improved through refractive surgery, which either reshapes the cornea or involves adding a lens.
Types of Refractive Surgeries
There are several types of refractive surgeries available, each tailored to address specific vision problems and patient needs. The most common procedures include:
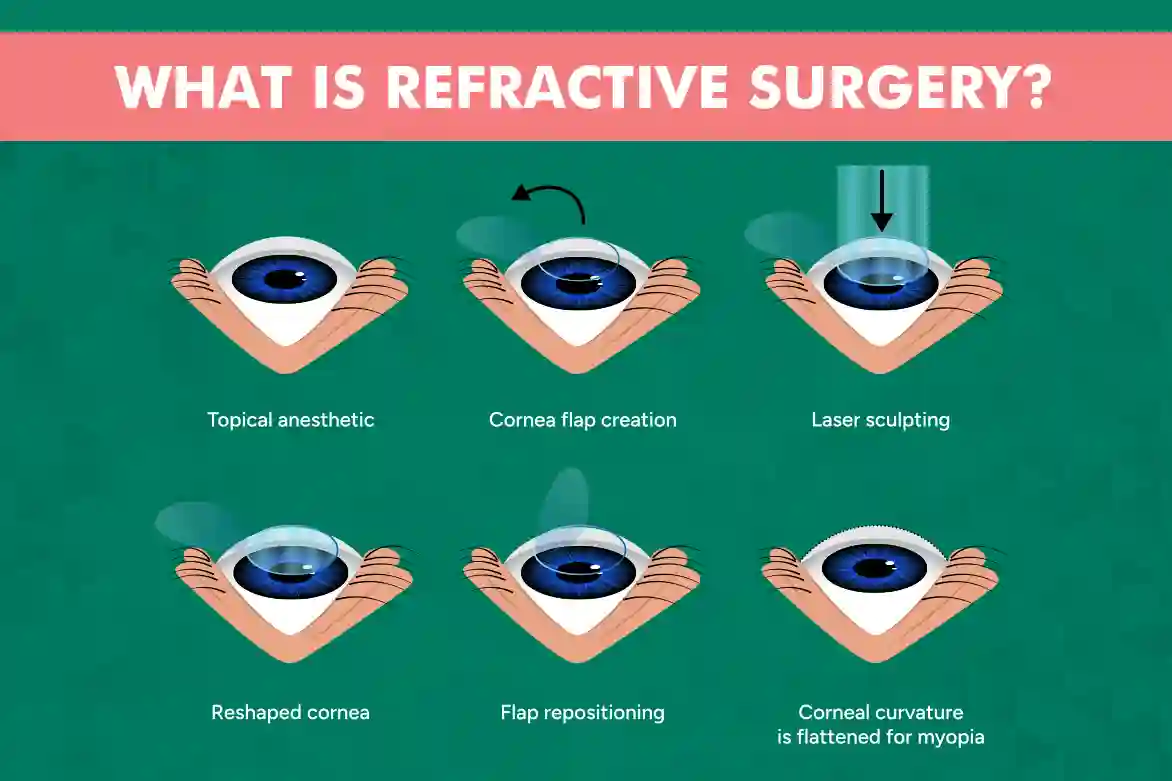
LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis):
A popular choice for correcting myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism, LASIK involves creating a flap in the cornea and reshaping the underlying tissue with a laser.
PRK (Photorefractive Keratectomy):
Similar to LASIK but without creating a corneal flap, PRK is ideal for patients with thinner corneas.
LASEK (Laser Epithelial Keratomileusis):
Combines elements of LASIK and PRK, making it suitable for patients with specific medical conditions.
SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction):
This procedure is a minimally invasive surgery primarily used to treat myopia. It involves creating a small incision in the cornea to remove a lenticule, a tiny piece of corneal tissue, which reshapes the cornea and corrects vision.
SILK (Smooth Incision Lenticule Keratomileusis):
The most advanced technique that also corrects astigmatism along with myopia. SILK involves creating a lenticule beneath the epithelial layer of the cornea. This method aims to preserve corneal strength and integrity while providing precise vision correction.
ICL (Implantable Collamer Lens):
Another effective option, where an artificial lens is surgically implanted inside the eye, providing a reversible solution for those with high myopia or thin corneas.
The Procedure: What to Expect
Before undergoing refractive surgery, patients will have a comprehensive eye examination to determine the most appropriate procedure. The surgery itself is typically quick, often taking less than 30 minutes per eye.
Most procedures involve the use of numbing eye drops, and patients remain awake throughout. Post-surgery, patients may experience mild discomfort and blurry vision, but these symptoms usually subside within a few days.
Benefits and Risks of Refractive Surgery
Benefits of Refractive Surgery:
- Significantly improved vision, reducing or eliminating the need for glasses or contact lenses.
- Enhanced quality of life and convenience due to not managing corrective eyewear.
- Quick recovery time, with noticeable vision improvement shortly after the procedure.
- Long-term solution with lasting results for many years.
- Potential increase in self-confidence as patients feel more comfortable without glasses.
Risks of Refractive Surgery:
- Dry eyes, which can cause discomfort and may require ongoing treatment.
- Visual disturbances such as glare and halos, especially at night, affect activities like driving.
- Risk of infection, which could lead to serious complications if not treated promptly.
- Possibility of under-correction or over-correction, leading to the need for additional procedures.
It is crucial to discuss these potential risks with your eye surgeon to make an informed decision about undergoing the procedure.
Is Refractive Surgery Right for You?
Refractive surgery is a good option for many people, but it’s not suitable for everyone. Ideal candidates are typically over 18, have stable vision prescriptions, and are free from certain eye conditions or diseases.
A thorough consultation with an eye care professional can help determine if refractive surgery is the best choice for your vision needs and lifestyle.
Choosing the Right Refractive Surgery: What You Need to Know
Selecting the right type of refractive surgery involves considering various factors such as your specific vision problem, corneal thickness, overall eye health, and personal preferences.
Consult with an experienced eye surgeon who can evaluate your condition and recommend the most suitable procedure to achieve the best possible outcome for your vision.
Conclusion
Refractive surgery offers a promising solution for those looking to enhance their vision and reduce reliance on corrective lenses. With various types of procedures available, it’s essential to understand your options and work with a qualified eye care professional to determine the best approach for your needs.
Whether you’re considering LASIK, PRK, or another type of refractive surgery, achieving crystal-clear vision is within reach.
FAQs
What is the recovery time for each type of refractive surgery?
Most patients recover within 1-3 days for SILK, SMILE, & LASIK, while PRK takes about 1-2 weeks for full recovery.
Which surgery is best for myopia, hyperopia, or astigmatism?
SILK and SMILE are ideal for myopia, LASIK and PRK for hyperopia, and Contoura Vision or LASIK for astigmatism.
Can refractive surgery be redone if vision changes over time?
Yes, enhancement procedures can be done if your cornea has sufficient thickness and your eyes meet the criteria.
Are there age limits for refractive surgery?
Candidates must be at least 18 years old, with stable vision for a year. There’s no strict upper limit but depends on eye health.
What are the risks associated with each type of refractive surgery?
Risks include dry eyes, glare, halos, or rare complications like under- or overcorrection. Compared to PRK or LASIK, SILK and SMILE have minimal risks.
How long do the results of refractive surgery last?
Results are typically permanent, but age-related changes like presbyopia or cataracts can affect vision later in life.
Is one type of surgery more painful than others?
LASIK and SMILE are painless, while PRK may cause mild discomfort during the initial recovery period.
Can refractive surgery correct presbyopia (age-related farsightedness)?
Yes, options like monovision LASIK or lens-based surgeries like RLE can help correct presbyopia.
How do I prepare for refractive surgery?
Stop wearing contact lenses 1-2 weeks before surgery, avoid makeup or lotions on surgery day, and follow your surgeon’s instructions.
Is refractive surgery covered by insurance?
It is considered elective, so most insurance plans do not cover it. Check with your provider for exceptions.